
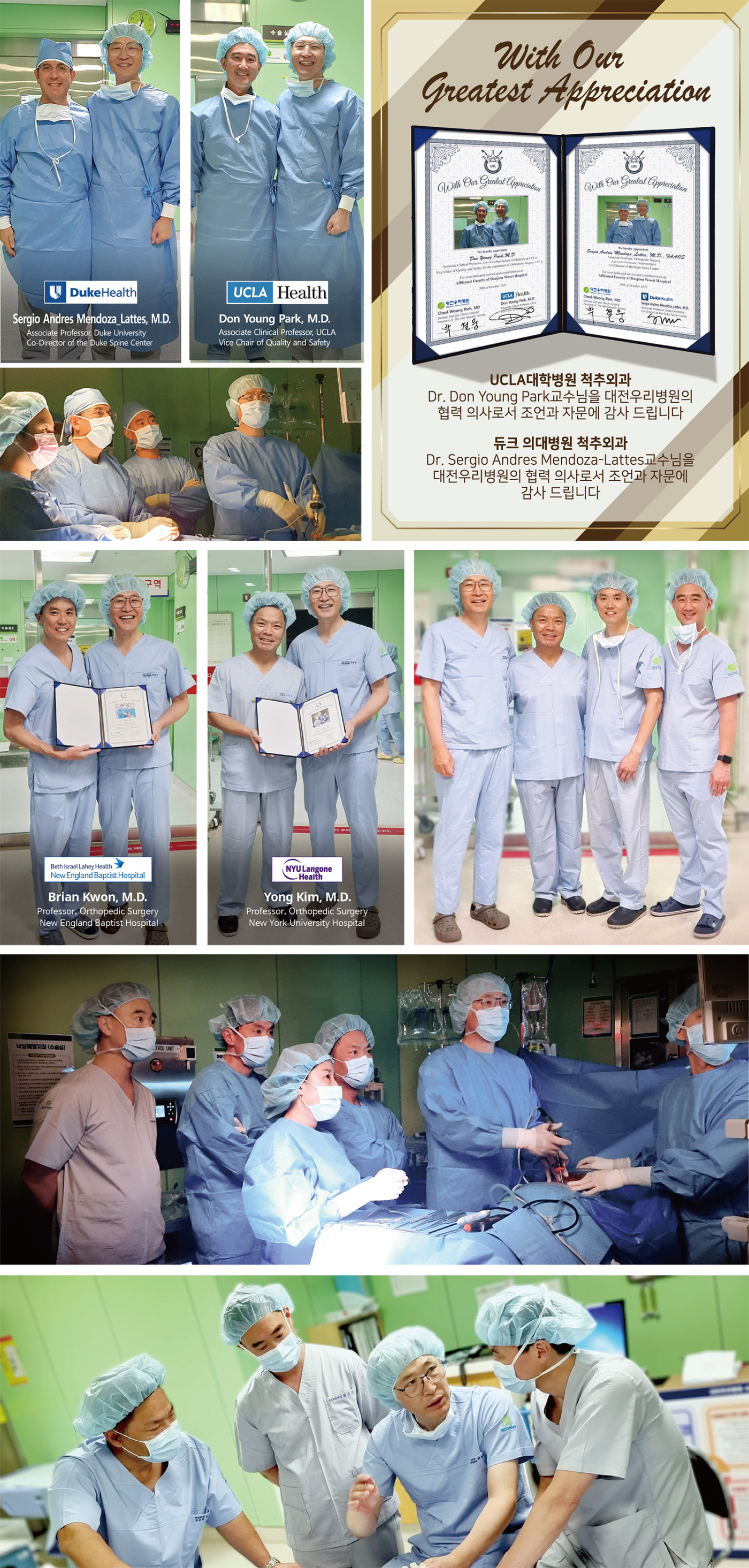
Daejeon Woori Hospital has been designated a specialist hospital by the Ministry of Health and Welfare for the fifth consecutive time. It has achieved accreditation from the Ministry of Health and Welfare for the third consecutive time, establishing itself again as the only safe spine specialist hospital in the central region.
The Ministry of Health and Welfare introduced the specialist hospital designation system in 2011 to nurture small and medium-sized hospitals with expertise and capacity in specific diseases or medical fields, alleviate the patient concentration phenomenon in large hospitals, and provide high-quality medical services to patients. The Ministry has designated 94 medical institutions as specialist hospitals for the first year of the fifth phase (2024~2026) after evaluating comprehensive medical performance based on patient composition ratios, volume of medical treatment, number of beds, mandatory medical fields, medical personnel, medical quality assessment, and medical institution certification over the past three years.
Daejeon Woori Hospital is equipped with a cooperative system of 21 specialists across seven medical departments and introduced robot-assisted joint surgery in 2023. It utilizes advanced medical devices to provide precise and safe customized medical services for patients. Through continuous research, the hospital has published globally recognized spinal treatment papers and lectured on advanced surgical techniques at international academic conferences, solidifying its position as a spine specialist hospital by striving for patient safety and improved medical technology.
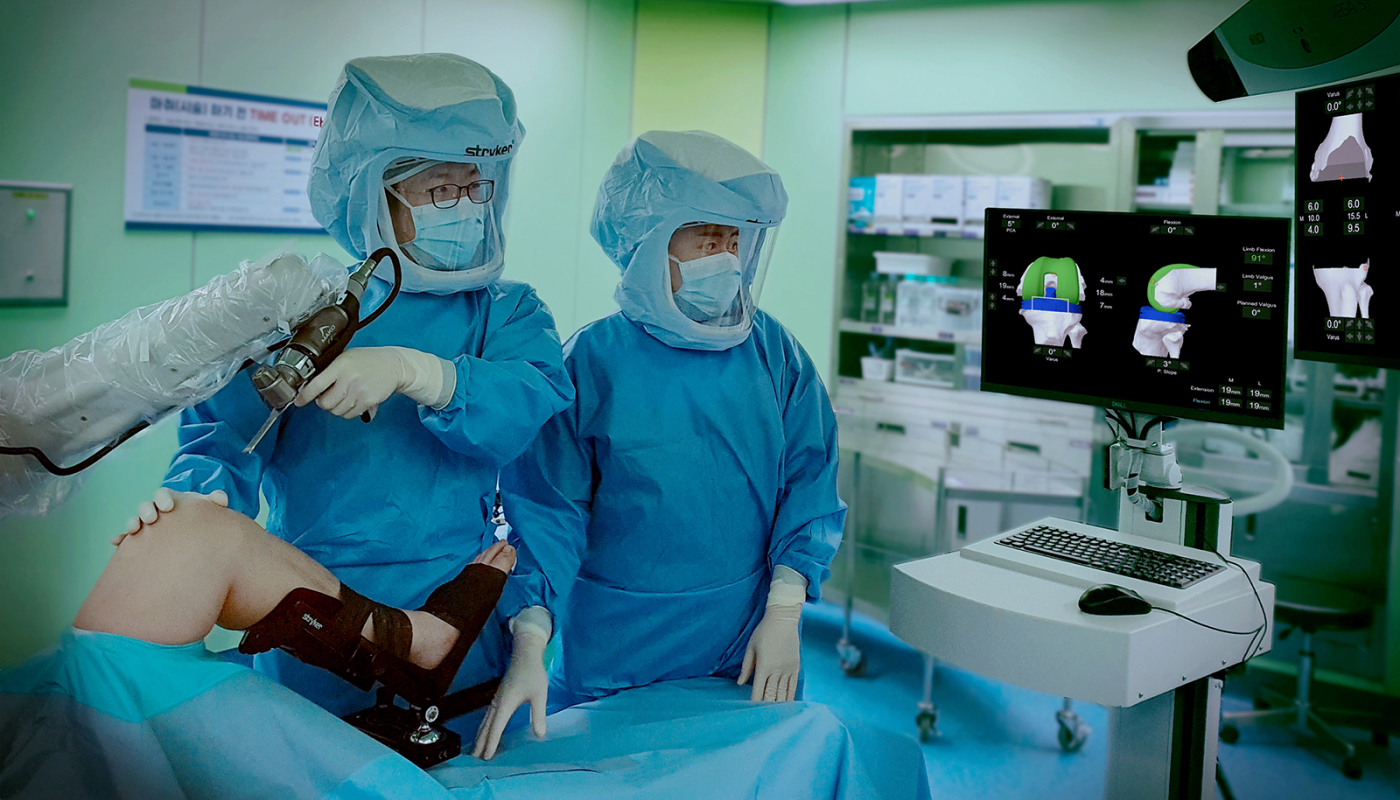
Introduction of FDA-Approved Robotic Joint Surgery
Daejeon Woori Hospital is the first in the central region to introduce the 'Mako SmartRobotics,' a joint surgery robot approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Mako Robotics has been simultaneously approved by the FDA and introduced in over 29 countries worldwide, with over 1,000 units deployed. It has demonstrated its safety through 15 years of clinical experience and over 500,000 cumulative surgeries.
Before surgery, a 3D CT scan captures the surgical area from various angles, analyzing the structure of the patient's knee to plan the size of the artificial joint, insertion angle, and cutting range. During surgery, real-time patient data comparison allows for accurate and precise surgery. Moreover, compared to conventional joint surgeries, it results in less bleeding, reducing the risk of infection and complications, minimizing damage to normal soft tissues, thereby reducing post-surgical pain and enabling effective rehabilitation, realizing a high-quality and safe medical service.


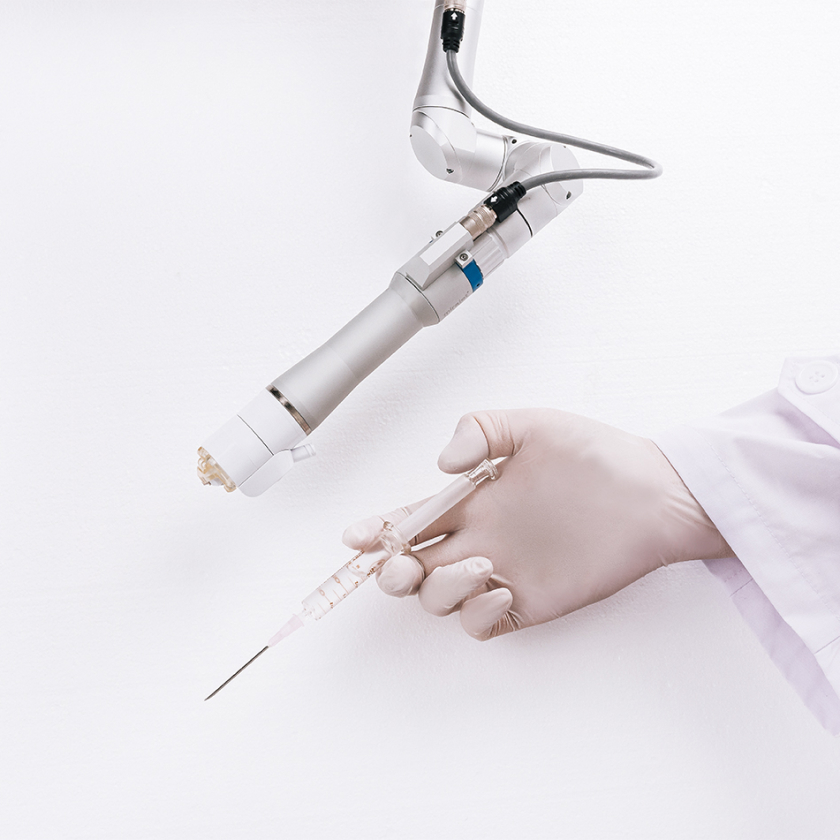
 Wellness Service
Wellness Service
 Bio Technology
Bio Technology
 Medical tourism
Medical tourism
 Festival & Mice
Festival & Mice
 Hot Issue
Hot Issue
 Interview With
Interview With
 Medical Technology
Medical Technology
 City & Culture
City & Culture
 Food & Travel
Food & Travel
 Health & Wellness Tips
Health & Wellness Tips
 Hot Issue
Hot Issue